work vs power example
The SI unit of power is Watt W. Power P 75 W.

Conservation Of Energy Example No 2 Conversion Of Potential And Kinetic Energy Final Velocity Potential Energy Physics Topics Energy
The SI unit of work is Joule J.

. The SI Unit of work is Joules J. Solved Example Problems for Unit of power Example 418. Thus the man doing same work in 5 seconds is more power full.
We define the capacity to do the. Power is the work done per unit of time. Example 1 - Calculating Work and Power A person pushes a cardboard moving box full of clothes which has a mass of 25 kilograms across the floor with 350.
1W x 1 s 1 Watt Second. Power is the rate at which that work is done. Calculate the energy consumed in electrical units when a 75 W fan is used for 8 hours daily for one month 30 days.
Below is a table of differences between Work and Energy. F is measured in newtons N. Power uses another unit that is horsepower which is equal to 746 Watt.
Work done does not depend on time. Watt is the power required to one joule of work in a second. Worked Example Applying the WorkEnergy Theorem An ice skater with a mass of 50 kg is gliding across the ice at a speed of 8 ms when her friend comes up from behind and gives her a push causing her speed to increase to 12 ms.
Displacement dr 15 m. Power is the amount of energy that is transferred in a unit of time. Work represents the amount of energy transferred when doing something.
The formula of calculating power WorkTime. However power just shows us the time that the work requires. For example same work is done by two different people with different time.
An object can have a value for the power without doing any work. Some examples of power are. For example a person pressing against a brick wall is consuming energy but no work is being done and no power created because the wall does not move.
If the object does any work the value of the power cannot be zero. You must have energy to accomplish work - it is like the currency for performing work. Work and power are similar to each other as both use energy.
Power is known as the amount of degree at which work is done. The formula for calculating the force is Work Force Displacement. Work is the energy needed to apply a force to move an object a particular distance where force is parallel to the displacement.
Sin37º0 6 and cos37 º0 8 Since the box moves in X direction we should find the X and Y components of the applied force. Power represents how fast the energy was transferred. Work can be done in various other measures like kWh MWh GWh and volt eV.
Find the work done by the force. Work is measured in joules whereas power is measured in watts. Work done by a force is equal to the product of force and the displacement in the direction of force.
Work done W Fdr cos θ. Is the rate of doing work or the rate of using energy which are numerically the same. Power is the work done per unit of time.
Say one of them does the work in 5 seconds and the other does in 8 seconds. Work is the distance traveled by the object in the direction of the force applied whereas the energy acts as the force and it refers the ability of the object to produce or create work. Power is the rate at which work is done.
In exercise its the rate of performing muscular work with potential energy becoming work aka moving weight or heat aka you getting warm. To do 100 joules of work you must expend 100 joules of energy. Main Differences Between Work and Power Work is the energy required to move an object whereas power is meant as the energy spent to move the object.
If you do 100 joules of work in one second using 100 joules of energy the power is 100 watts. Work force Displacement. The formula for power is P W T P Power W Work done and T Time taken Horse Power.
Work is energy or force used to move an object from one place to another. Time of usage t 8 hour 30 days 240 hours. The symbol of work is W.
The SI unit of power is Watt W. Power is the rate of energy consumed in a unit of time Power Work time. Work is the displacement of an object when a force push or pull is applied to it.
Example 25 N force is applied to a box and box moves 10m. Now let us look at the formulas that differentiate work from power. This is easier to understand if you realize that Work Force x Distance.
Power spent depends on the time in which work is done. 60 Watt power bulbs spend 60 Joules of energy or a car accelerating which does work and consumes large amounts of fuel etc. James Watt was the developer of steam engines.
Electrical energy consumed is the product of power and time of usage. An object can have a value for the power without doing any work. W 125 60 J.
Work is measured in joules whereas power is measured in watts. This article discusses work energy and power in detail. Power of a source is the raw of doing work by it.
Difference between work and power is based on the amount and rate of energy consumed. Whereas power is the amount of energy transferred or converted in unit time. Work is known as the total amount of energy used to move an object from one place to another with external force.
Power is denoted by P. Or we can I horsepower 075 KW. Energy is a measurement of the ability of something to do work.
It is the rate of work done or rate of energy transfer.

Pin By Kimberly Rubiolo Miller On Workin Stakeholder Analysis Learning And Development Analysis

Work Power And Energy Worksheet 7 1 Potential And Kinetic Energy Cpo Science Pages 1 29 Energy Transformations Potential Energy Kinetic And Potential Energy

Where There Are No Opposing Forces A Moving Body Needs Noforce To Keep It Moving With A St Potential Energy Kinetic And Potential Energy Work Energy And Power

A Coaching Power Tool Created By Jose Antonio Villalobos Sarria Monologues Leadership Coaching Power Tools

Kinetic Energy Definition Formula Concepts Examples Kinetic Energy Energy Kinetic

8 Energy Work And Power Worksheet Key Calculating Work Physics Answers Work Energy And Power

50 Potential Versus Kinetic Energy Worksheet Chessmuseum Template Library Energy Science Lessons Kinetic Energy Activities Physical Science

Infographic Potential Vs Kinetic Energy Kids Discover Energy Kids Kinetic Energy Physical Science
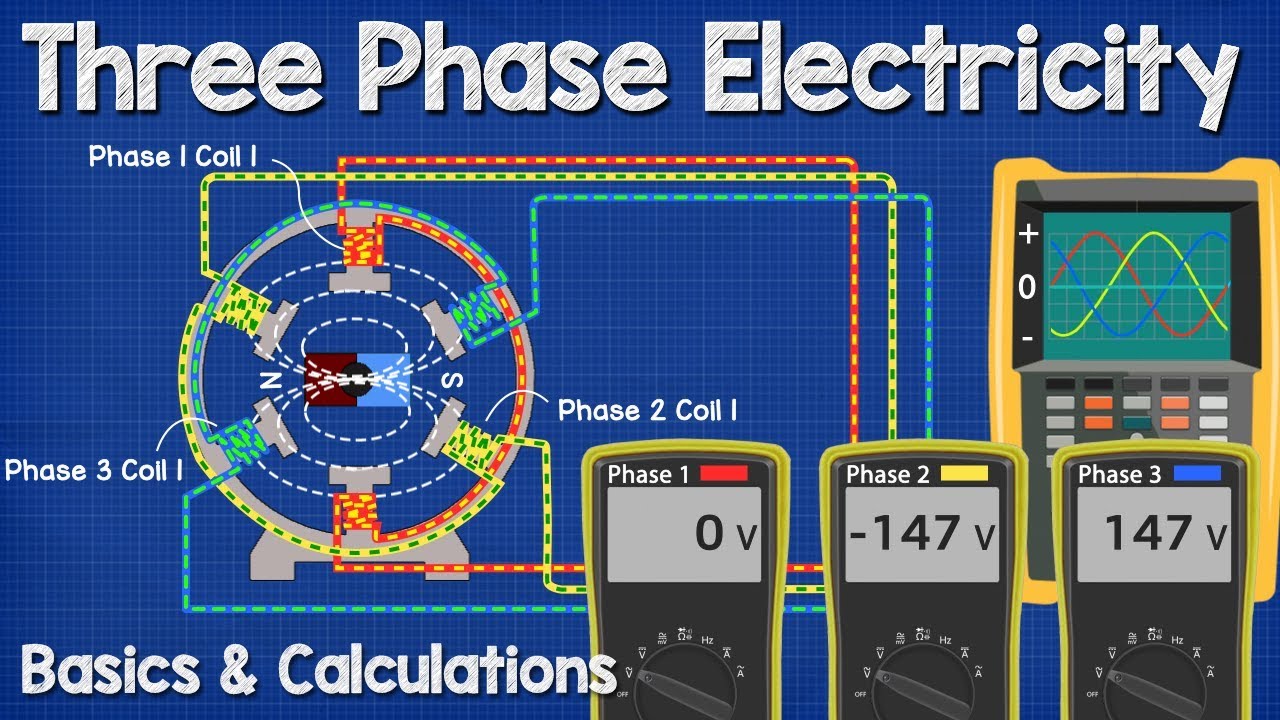
Three Phase Electricity Basics And Calculations Electrical Engineering Youtube Electrical Engineering Electromechanical Engineering How Electricity Works

Work Energy And Power Cbse Notes For Class 11 Physics 14 Physics Work Energy And Power Mechanical Energy

Energy Work Power Net Work Done On A Object

Physics Of Work And Power Flash Cards Work Energy And Power Power Physics Physics Lessons

Easy To Remember The Forms Of Energy Education Quotes For Teachers Physics Online Tutoring

Work Energy And Power Physics Lessons Physics Notes How To Study Physics

Conservation Of Energy Conversion Of Potential Energy To Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Physics Topics Energy Work



